Summer comes around the corner and you just can't help but look forward to the heat on your skin. Before you book that next beach trip or you start preparing your backyard for a suntan session, you need to familiarize yourself with UV Radiation and how it can affect your skin.
Ultra Violet Radiation or UV Radiation is a type of non-ionizing radiation produced by the sun but it can also be found in artificial sources such as tanning beds. The most natural source of UV radiation is the sun, which is something none of us can avoid being exposed to.
When summer comes along we find ourselves racing out to bask in the heat, but we might want to start taking some extra precautions.
Too much UV radiation exposure can lead to pretty nasty sunburn, eye damage, and even skin cancer. To know how to protect our skin, let’s educate ourselves on what UV radiation is and how we can be healthier around it!
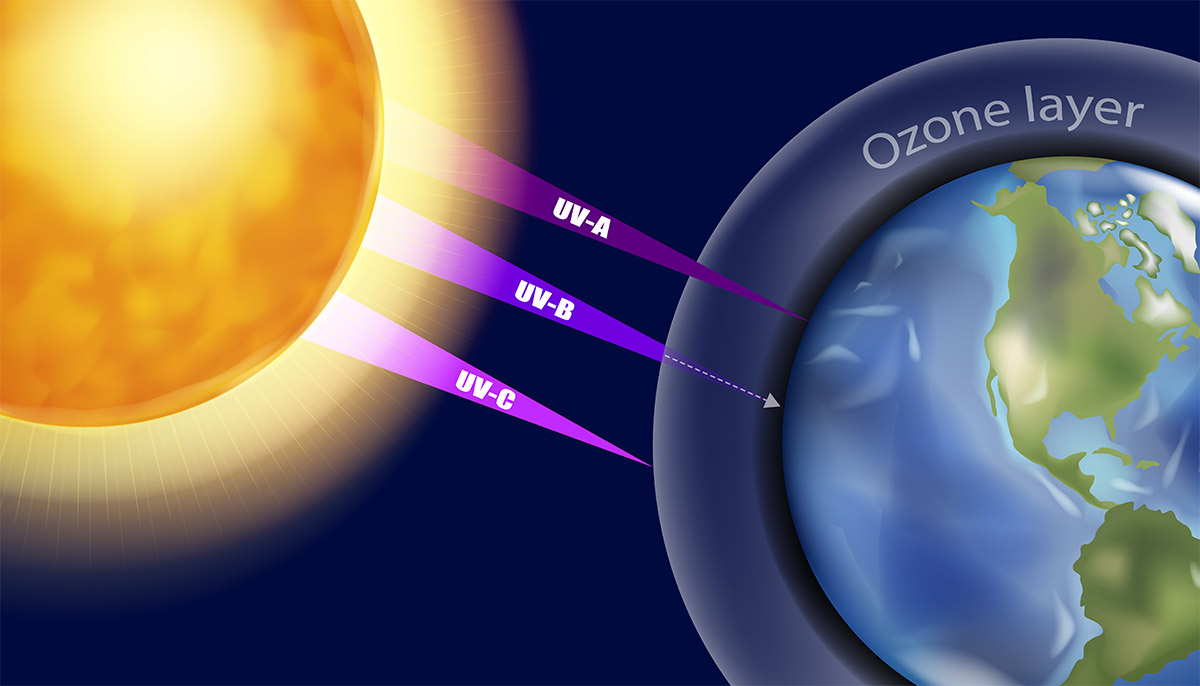
There are three types of UV radiation rays: ultraviolet A (UVA), ultraviolet B (UVB), and ultraviolet C (UVC). These types have different wavelengths and therefore have different effects on your health.
| Wave Type | Wavelength | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| UVA | 315- 399 nm | UVA accounts for 95% of the UV radiation reaching earth. Recent studies show that UVA is highly responsible for the development of skin cancer since this can penetrate in the deep layers of the skin. |
| UVB | 280-314 nm | UVB is the most biologically active but this cannot penetrate beyond the skin layers. However, UVB has effects when it comes to faster skin and aging and may promote skin cancer growth. Most of the solar UVB is filtered by the atmosphere. |
| UVC | 100-279 nm | UVC is the most damaging type among the three. However, UVC is completely filtered out by the atmosphere and humans are most likely never to be of contact. |
(Source: Center for Disease Control and Prevention and World Health Organization)
One of the most alarming effects of prolonged UV radiation exposure is the promotion of skin cancer. Studies have shown that most basal and squamous cell skin cancers have a high correlation to individuals with a lifestyle commonly involving too much sun exposure.
Other health problems may also arise such as:
In moderate amounts, UV rays can be good for you. Human skin makes vitamin D naturally when it is exposed to the sun's UV rays which helps your overall health.
Making sure that you are kept under a high-quality shade when outside can reduce the risks of health problems while you enjoy being out in the sun!
Choice report finds popular Australian sunscreens fail to meet SPF claims on label
Consumer group Choice tested 20 sunscreens and found only four provided the SPF protection their label claimed.